Introduction to Business Finance
Business Finance is also known as Financial Management. Financial management is management principles and practices applied to finance. General management functions include planning, execution and control.
Financial decision making includes decisions as to size of investment, sources of capital, extent of use of different sources of capital and extent of retention of profit or dividend payout ratio. Financial management, is therefore, planning, execution and control of investment of money resources, raising of such resources and retention of profit/payment of dividend.
According to Guthamann and Dougall,” Business finance can be broadly defined as the activity concerned with the planning, raising, controlling and administering the funds used in the business.”
About Business Finance MCQs
In this post you will get Business Finance MCQs which are especially for UGC NET and SET exams of various states such as SLET NE, GSET, WBSET. JKSET, Rajasthan SET, MP SET, MH SET, KSET and Kerala SET.
We try to cover all the questions asked in above mentioned exams relating to Business Finance MCQs. Visit our website regularly for latest contents.
Business Finance MCQs for UGC NET and SET Exams
1. Physical delivery of Foreign Exchange has to take place in case of: [GSET]
(A) Forward Market.
(B) Spot Market.
(C) Future Market.
(D) Options Market.
Ans: (B) Spot Market.
2. Which among the following is the correct character of the foreign exchange market? [GSET]
(A) Foreign exchange market is domestic market.
(B) Foreign exchange market is operated within a country.
(C) Foreign exchange market is dynamic and round the clock market.
(D) Foreign exchange market is used only for trade related transactions.
Ans: (C) Foreign exchange market is dynamic and round the clock market.
3. With fixed cost of Rs. 400, a firm has average total costs of Rs. 3 and average variable cost of Rs. 2.50. Its output is _______. [GSET]
(A) 200 units.
(B) 400 units.
(C) 800 units.
(D) 1600 units.
Ans: (C) 800 units.
4. Contribution is the difference between: [GSET]
(A) Sales value and variable costs of sales.
(B) Sales value and fixed costs of sales.
(C) Sales value and period costs of sales.
(D) Sales value and overhead costs of sales.
Ans: (A) Sales value and variable costs of sales.
5. If you know that with 8 units of output, average fixed cost is Rs. 12.50 and average variable cost is Rs. 81.25, then total cost at this output level is _______. [GSET]
(A) Rs. 93.75.
(B) Rs. 97.78.
(C) Rs. 750.
(D) Rs. 880.
Ans: (C) Rs. 750.
6. One of the crucial assumptions of Walter model of dividend distribution and firm value is that the firm finances its all investments through [GSET]
(A) external debt (raised for investment).
(B) external equity (raised for investment).
(C) retained earnings.
(D) external commercial borrowings.
Ans: (C) retained earnings.
Also Read: UGC NET EXAM: Paper 08 Commerce MCQs
- Business Environment MCQs
- Accounting and Auditing MCQs
- Business Economics MCQs
- Business Finance MCQs
- Business Management MCQs
- Human Resource Management MCQs
- Bank and Financial Institution MCQs
- Marketing Management MCQs
7. A Joint Stock Company is managed by the Board of Directors elected by: [GSET]
(A) Top Management.
(B) Shareholders.
(C) Employees of Company.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (B) Shareholders.
8. Convertible bond is: [GSET]
(A) Debt + Warrant.
(B) Debt + Cash.
(C) Debt + Share.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (C) Debt + Share.
9. Trading on equity means: [GSET]
(A) The use of long-term fixed interest bearing debt and preference share capital.
(B) The use of long-term fixed interest bearing debt and equity share capital.
(C) The use of long-term fixed interest bearing debt and preference share capital along with equity share capital.
(D) The use of long-term fund and short-term fund.
Ans: (C) The use of long-term fixed interest bearing debt and preference share capital along with equity share capital.
10. Capital budgeting is the process of making investment decisions on: [GSET]
(A) Total expenditure.
(B) Revenue expenditure.
(C) Capital expenditure.
(D) Preliminary expenditure.
Ans: (C) Capital expenditure.
11. The Accounting Rate of Return is also known as: [GSET]
(A) Return on preference share.
(B) Return on capital employed.
(C) Return on debt.
(D) Return on equity share.
Ans: (B) Return on capital employed.
12. The appropriate objective of an enterprise is: [GSET]
(A) Maximisation of profit.
(B) Maximisation of sales.
(C) Maximisation of owner’s wealth.
(D) Maximisation of assets.
Ans: (C) Maximisation of owner’s wealth.
13. Gearing Ratio indicates: [GSET]
(A) The relationship between short-term funds and long-term funds.
(B) The relationship between preference share and equity share.
(C) The relationship between loan funds and net worth.
(D) The relationship between debenture and loan.
Ans: (C) The relationship between loan funds and net worth.
14. The correct formula of Walter’s dividend model is: [GSET]
(A) P = D/Ka = 9.
(B) P = D/Kg.
(C) P = D/Ke.
(D) P = D/Kg = a.
Ans: z
15. If the capital budgeting decision (a project) generates constant cash flows each year then payback period = [GSET]
(A) Annual cash flows/Initial investment.
(B) Initial Investment/Annual cash flows.
(C) Present value of annual cash flows/Initial investment.
(D) Present value of annual cash flows/present value of initial investment.
Ans: (B) Initial Investment/Annual cash flows.

17. In case of ‘Zero interest Fully Convertible Debentures’, (ZFCD) return to debenture holders is available in the form of [GSET]
(A) Difference between the issue price of ZFCD and the market price of converted share.
(B) Difference between the issue price of ZFCD and the redemption value given by the company.
(C) Interest over the life ZFCD.
(D) Interest + difference between the issue price of ZFCD and redemption value.
Ans: (A) Difference between the issue price of ZFCD and the market price of converted share.
18. Capital structure designing has nothing to do with: [GSET]
(A) Profitability.
(B) Flexibility.
(C) Corporate Governance.
(D) Liquidity.
Ans: (C) Corporate Governance.
19. Capital structure refers to: [GSET]
(A) Equity financing of a firm.
(B) Debt financing of a firm.
(C) Permanent financing of a firm.
(D) Working capital financing of a firm.
Ans: (C) Permanent financing of a firm.
20. Arbitrage takes advantage of: [GSET]
(A) Different Exchange rates in same market.
(B) Same Exchange rate in different market.
(C) Different Exchange rates in different market.
(D) All of the above.
Ans: (C) Different Exchange rates in different market.
21. Exchange rate relate to demand and supply of: [GSET]
(A) Foreign goods.
(B) Foreign money.
(C) National money.
(D) National goods in relations to foreign goods.
Ans: (C) National money.
22. What is the popular term used for that type of option in Foreign Exchange Market which provides the holder the right to purchase or sell foreign currency at the most favourable exchange rate realized over the life of the option? [GSET]
(A) Forward reversing option.
(B) Look-back option.
(C) Preference option.
(D) Basket option.
Ans: (B) Look-back option.
23. Which of the following is not a component of Credit Risk? [GSET]
(A) Payment Default.
(B) Exchange Rate Fluctuations.
(C) Counter Party Risk.
(D) Political Risk.
Ans: (B) Exchange Rate Fluctuations.
24. Under Liberalized Exchange Rate Mechanism in India: [GSET]
(A) Exporters were allowed to retain part of their earnings in foreign exchange.
(B) Tourists were allowed to carry unlimited foreign exchange.
(C) Foreign exchange transactions for imports were restrained.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (A) Exporters were allowed to retain part of their earnings in foreign exchange.
25. Which of the following are the micro-economic variables that help to define and explain the discipline of finance? [GSET]
(A) Risk and return.
(B) Capital structure.
(C) Inflation.
(D) All of the above.
Ans: (D) All of the above.
26. The _______ is the percentage change in operating income that results from the percentage change in sales. [GSET]
(A) Degree of financial leverage.
(B) Break-even point.
(C) Degree of operating leverage.
(D) Degree of combined leverage.
Ans: (C) Degree of operating leverage.
27. The multiple IRR are possible when: [GSET]
(A) cash flows in the early stages of the project exceed cash flows during the later stages.
(B) Cash flows reverse their signs during the project life.
(C) Cash flows are uneven.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (B) Cash flows reverse their signs during the project life.
28. When a firm advises its customers to mail their payments to special post-office collection centres, the system is known as: [GSET]
(A) concentration banking.
(B) lock-box system.
(C) paying the float.
(D) post-office collection.
Ans: (B) lock-box system.
29. According to Net-operating income approach the average cost of capital: [GSET]
(A) declines as debt-equity ratio increases.
(B) increases as debt-equity ratio increases.
(C) remains constant irrespective of changes in debt-equity ratio.
(D) Keeps on fluctuating with increases in debt-equity ratio.
Ans: (C) remains constant irrespective of changes in debt-equity ratio.
30. Principal goal of financial management is considered to be the maximisation of: [GSET]
(A) Profit.
(B) Shareholders’ wealth.
(C) Earnings per share.
(D) Return on equity.
Ans: (B) Shareholders’ wealth.
31. Given: [GSET]
|
Operating Fixed Costs Sales P/V Ratio |
Rs. 25,000 Rs. 1,00,000 40% |
The operating leverage shall be:
(A) 1.50.
(B) 2.50.
(C) 2.67.
(D) 2.47.
Ans: (C) 2.67.
32. A company raises Rs. 1,00,000 by the issue of 1,000, 10% debentures of Rs. 100 each repayable at par after 10 years. If the corporate tax rate is 30%, what is the cost of debt capital to the firm: [GSET]
(A) 7%.
(B) 7.5%.
(C) 9%.
(D) 10%.
Ans: (A) 7%.
33. Financing current assets involves the following, except: [GSET]
(A) Determining the level of current assets.
(B) Evaluating alternative policies of financing.
(C) Determining the level of fixed assets.
(D) Finding an appropriate source with regard to cost and risk.
Ans: (C) Determining the level of fixed assets.
34. The objective of a good dividend policy is to: [GSET]
(A) Maximize the value of the firm.
(B) Minimize the amount to be retained.
(C) Iron out the fluctuations in earnings.
(D) Prevent transfer of shares.
Ans: (A) Maximize the value of the firm.
35. Which of the following does not explain relationship between capital structure and the value of the firm? [GSET]
(A) Net Income Approach.
(B) Net Operating Income Approach.
(C) Net Operating Leverage Approach.
(D) Modigliani-Miller Hypothesis.
Ans: (C) Net Operating Leverage Approach.
36. If EBIT = Rs. 15,00,000, Interest Rs. 1,50,000, and Corporate tax = 40%, then degree of financial leverage shall be: [GSET]
(A) 1.11.
(B) 1.21.
(C) 1.31.
(D) 1.41.
Ans: (A) 1.11.
37. The balance of debtors is not influenced by: [GSET]
(A) Level of sales.
(B) Collection policy.
(C) No. of employees in Credit Dept.
(D) Credit terms.
Ans: (C) No. of employees in Credit Dept.
38. Which of the following is not a determinant of dividend policy? [GSET]
(A) Legal constraints and liquidity of the firm.
(B) Financial position of the shareholders.
(C) Retention policy and future financing.
(D) Business cycle and inflation.
Ans: (B) Financial position of the shareholders.
39. For discounted cash-flow methods, the discount rate used is [GSET]
(A) fixed arbitrarily.
(B) equivalent to bank rate.
(C) equivalent to firm’s average cost of capital.
(D) equivalent to final rate of dividend.
Ans: (C) equivalent to firm’s average cost of capital.
40. Operating leverage increases, when: [GSET]
(A) Variable cost increases.
(B) Fixed cost increases.
(C) Variable cost decreases.
(D) Fixed cost decreases.
Ans: (B) Fixed cost increases.
41. Given the constant Ke and Kd and Kd < Ke, the WACC (K0) will decrease continuously with increase in financial leverage measured by Debt/value is given by [GSET]
(A) Net income approach.
(B) Net operating income approach.
(C) M-M hypothesis proposition-I.
(D) Traditional Theory.
Ans: (A) Net income approach.
42. The most important goal of financial management is: [GSET]
(A) Profit maximisation.
(B) Matching income and expenditure.
(C) Using business assets effectively.
(D) Wealth maximisation.
Ans: (D) Wealth maximisation.
43. A project having discount rate of 10% has the following cash-flows: [GSET]
|
Year |
Cash flows (Rs. Lacs) |
|
0 1 2 3 |
– 50 60 – 30 80 |
The NPV of the product is:
(A) Rs. 39.84 Lakhs.
(B) Rs. 39.48 Lakhs.
(C) Rs. 40.48 Lakhs.
(D) Rs. 93.84 Lakhs.
Ans: (A) Rs. 39.84 Lakhs.
44. PQR Ltd. has taken a term loan of Rs. 20 lakhs at an interest rate of 14% p.a. If the tax rate applicable is 30%, the cost of term loan is: [GSET]
(A) 8.9%.
(B) 9.8%.
(C) 14.0%.
(D) 4.2%.
Ans: (B) 9.8%.
45. In Miller-Orr model of cash management: [GSET]
(A) The lower limit of cash balance is set by the management and the upper limit and return point for cash balance are derived.
(B) The lower limit and the upper limit of cash balance are pre-decided by the management and return point for cash balance is derived.
(C) The lower limit for cash balance and the return point for the cash balance are pre-decided by the management and upper limit for cash balance is derived.
(D) Both upper limit for cash balance and return point for cash balance are pre-decided by the management and lower limit for cash balance is derived.
Ans: (A) The lower limit of cash balance is set by the management and the upper limit and return point for cash balance are derived.
46. According to net income approach, the average cost of capital of firm: [GSET]
(A) declines as debt-equity ratio increases.
(B) increases as debt-equity ratio increases.
(C) remains constant irrespective of change in debt-equity ratio.
(D) keeps on fluctuating with increase in debt-equity ratio.
Ans: (A) declines as debt-equity ratio increases.
47. Which one is not an important objective of Financial Management? [GSET]
(A) Profit Maximisation.
(B) Wealth Maximisation.
(C) Value Maximisation.
(D) Maximisation of Social Benefits.
Ans: (D) Maximisation of Social Benefits.
48. The cost of capital of a firm is: [GSET]
(A) The maximum rate of return from investments.
(B) The minimum rate of return from investments.
(C) The maximum rate of return on equity.
(D) The minimum rate of return on equity.
Ans: (B) The minimum rate of return from investments.
49. Capital Budgeting is also known as _______. [GSET]
(A) Investment Decision-making.
(B) Capital Expenditure Decision.
(C) Planning Capital Expenditure.
(D) All of the above.
Ans: (D) All of the above.
50. Which of the following terms is used to represent the proportionate relationship between debt and equity? [GSET]
(A) Cost of Capital.
(B) Capital Budgeting.
(C) Assets Structure.
(D) Capital Structure.
Ans: (D) Capital Structure.
51. Gordon’s model relates to: [GSET]
(A) Reserve Policy.
(B) Capital Policy.
(C) Fund Policy.
(D) Dividend Policy.
Ans: (D) Dividend Policy.
52. Gordon’s model is related with: [GSET]
(A) Market Policy.
(B) Capital Policy.
(C) Dividend Policy.
(D) Reserve Policy.
Ans: (C) Dividend Policy.
53. According to MM Proposition, in the presence of corporate tax, the optimal capital structure would be 100% _______. [GSET]
(A) Equity.
(B) Debt.
(C) Bonds.
(D) Debentures.
Ans: (B) Debt.
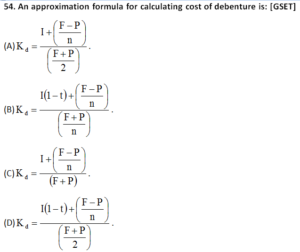
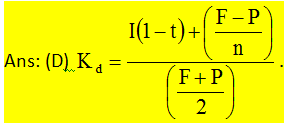
55. If the Net Present Value for a project is negative, then: [GSET]
(A) IRR = Cost of capital.
(B) IRR < Cost of capital.
(C) IRR > Cost of capital.
(D) BCR = 1.
Ans: (B) IRR < Cost of capital.
56. Baumol’s Cash Management Model attempts to minimize: [GSET]
(A) Holding costs.
(B) Transaction costs.
(C) Cash balances.
(D) Total costs.
Ans: (D) Total costs.
57. Who developed one of the earliest models linking the value of the firm to its dividend policy? [GSET]
(A) Walter.
(B) Gorden.
(C) Miller.
(D) Modigliani.
Ans: (B) Gorden.
58. Capital Budgeting Decisions are: [GSET]
(A) Reversible Decisions.
(B) Strategic Investment Decisions.
(C) Short-term Investment Decisions.
(D) Tactical Investment Decisions.
Ans: (B) Strategic Investment Decisions.
59. Generally if the risk involved in a firm is higher: [GSET]
(A) Cost of capital will be lower.
(B) Cost of capital will be higher.
(C) Cost of capital will be neutral.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (B) Cost of capital will be higher.
60. Long-term sources of finance also required for _______ of working capital. [GSET]
(A) Economical.
(B) Costly.
(C) Beneficial.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (A) Economical.
61. According to which of the following, the firm’s market value is not affected by capital structure? [GSET]
(A) M.M. Hypothesis.
(B) Net Income Approach.
(C) The Traditional View.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (A) M.M. Hypothesis.
62. Match the following: [GSET]
|
(1) Convertible Debentures. (2) Secured Debentures. (3) Interest on the Debentures. (4) Irredeemable Debentures. |
(i) Holders have the right to recover their money from the sale of Assets. (ii) Deducted from the profits of the company. (iii) Permanent Liability on the company. (iv) The holders of such debentures are given the option to exchange them for share. |
Codes:
(A) (1)-(i), (2)-(ii), (3)-(iii), (4)-(iv).
(B) (1)-(ii), (2)-(iv), (3)-(i), (4)-(iii).
(C) (1)-(iv), (2)-(i), (3)-(iii), (4)-(ii).
(D) (1)-(iii), (2)-(iv), (3)-(ii), (4)-(i).
Ans: (C) (1)-(iv), (2)-(i), (3)-(iii), (4)-(ii).
63. The variability of EPS caused by the use of financial leverage is called: [GSET]
(A) Operating risk.
(B) External risk.
(C) Financial risk.
(D) Internal risk.
Ans: (C) Financial risk.
64. The returns foregone in the next best investment option is called: [GSET]
(A) Sunk cost.
(B) Marginal cost.
(C) Opportunity cost.
(D) Foregone cost.
Ans: (C) Opportunity cost.
65. In case where the available funds for investment are lower than the acceptable investment (after applying the appraisal criteria) the suitable additional appraisal criteria, for final decision-making will be: [GSET]
(A) NPV.
(B) Payback.
(C) ARR.
(D) Profitability index.
Ans: (D) Profitability index.
66. The working capital requirements of the company even at the lowest level of its sales cycle is called: [GSET]
(A) Gross working capital.
(B) Permanent working capital.
(C) Net working capital.
(D) Fluctuating working capital.
Ans: (B) Permanent working capital.
67. According to Walter model, a firm should have 100% dividend payout ratio when: [GSET]
(A) r = ke.
(B) r < ke.
(C) r > ke.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (B) r < ke.
68. Match List-I with List-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below it: [GSET]
|
List-I |
List-II |
|
(1) Net Income approach. (2) Net operating income approach. (3) Traditional theory. (4) M.M. approach. |
(a) Ke is rising with increase in debt. (b) Ke and Kd remain constant irrespective of proportion of debt. (c) Arbitrage process. (d) Optimal capital structure. |
Codes:
(A) (1)-(b), (2)-(a), (3)-(d), (4)-(c).
(B) (1)-(a), (2)-(b), (3)-(c), (4)-(d).
(C) (1)-(c), (2)-(d), (3)-(b), (4)-(a).
(D) (1)-(d), (2)-(c), (3)-(a), (4)-(b).
Ans: (A) (1)-(b), (2)-(a), (3)-(d), (4)-(c).
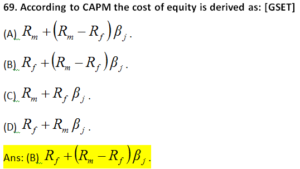
70. Match List-I with List-II and choose the correct option from the codes given below it: [GSET]
|
List-I |
List-II |
|
(1) Pay-back method. (2) NPV method. (3) IRR method. (4) Profitability Index method. |
(a) Shareholder wealth maximisation is directly examined. (b) There can be more than one outcome even in single calculation. (c) Useful in case of capital rationing. (d) Useful in case where rate of technological obsolescence is fast. |
Codes:
(A) (1)-(a), (2)-(d), (3)-(c), (4)-(b).
(B) (1)-(b), (2)-(c), (3)-(d), (4)-(a).
(C) (1)-(c), (2)-(b), (3)-(a), (4)-(d).
(D) (1)-(d), (2)-(a), (3)-(b), (4)-(c).
Ans: (D) (1)-(d), (2)-(a), (3)-(b), (4)-(c).
71. In the Miller-Orr model of optimum cash balance, return point value is: [GSET]
(A) inversely related to interest rate.
(B) inversely related to holding cost.
(C) inversely related to transaction cost.
(D) inversely related to cash flow variance.
Ans: (A) inversely related to interest rate.
72. According to the Gordon Model, the price of the share is dependent on: [GSET]
(A) Dividend pay-out ratio and earnings per share.
(B) The required rate of return by shareholders and expected rate of return on investment by firms.
(C) EPS at the end of the year, dividend pay-out ratio, rate of return required by shareholders and expected rate of return on investment by firm.
(D) Target pay-out ratio and EPS.
Ans: (C) EPS at the end of the year, dividend pay-out ratio, rate of return required by shareholders and expected rate of return on investment by firm.
73. Match the following of List I and List II and choose the correct option from the codes given below: [GSET]
|
List-I (Concepts) |
List-II (Disadvantages) |
|
(a) Joint Venture. (b) Foreign Trade. (c) Fixed Exchange Rate. (d) Flexible Exchange Rate. |
(1) It may exhaust resources. (2) Unnecessary capital movement. (3) The amount of profit potential are reduced. (4) Transient nature. |
Codes:
(A) (a)-(3), (b)-(1), (c)-(4), (d)-(2).
(B) (a)-(2), (b)-(1), (c)-(4), (d)-(3).
(C) (a)-(4), (b)-(3), (c)-(2), (d)-(1).
(D) (a)-(1), (b)-(2), (c)-(3), (d)-(4).
Ans: (A) (a)-(3), (b)-(1), (c)-(4), (d)-(2).
74. Which one of the following is not an advantage of the fixed exchange rate? [GSET]
(A) Protection from the risk of uncertainty.
(B) Maintenance of monetary discipline.
(C) Convenience.
(D) Transient nature.
Ans: (D) Transient nature.
75. According to purchasing power parity theory exchange rates are determined by: [GSET]
(A) Inflation rates.
(B) Interest rates.
(C) Relative prices.
(D) Demand and supply.
Ans: (C) Relative prices.
76. Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) are issued by the: [GSET]
(A) World Bank.
(B) R.B.I.
(C) I.D.A.
(D) I.M.F.
Ans: (D) I.M.F.
77. Foreign Exchange and Foreign Currencies in India are governed by: [GSET]
(A) R.B.I.
(B) Banking Regulation Act.
(C) FEMA (Act).
(D) SEBI Act.
Ans: (C) FEMA (Act).
78. A current account surplus represents: [GSET]
(A) Net Foreign investments.
(B) Net Foreign drain.
(C) Disinvestment Abroad.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (A) Net Foreign investments.
79. Match the following and find the appropriate choice from options: [GSET]
|
Theory |
Author |
|
(I) Overlapping Product Ranges. (II) Product Cycle Theory. (III) Internal and External theories of scale. (IV) Competitive advantages of Nation. |
(1) Michael Porter. (2) Paul Krugman. (3) Raymond Vernon. (4) Linder. |
Codes:
(A) (I)-(1), (II)-(3), (III)-(4), (IV)-(2).
(B) (I)-(4), (II)-(3), (III)-(2), (IV)-(1).
(C) (I)-(1), (II)-(2), (III)-(3), (IV)-(4).
(D) (I)-(3), (II)-(4), (III)-(2), (IV)-(1).
Ans: (B) (I)-(4), (II)-(3), (III)-(2), (IV)-(1).
80. The aim of foreign exchange risk management is to: [GSET]
(A) Maximize profits.
(B) Earn a minimum level of profit.
(C) Minimize losses.
(D) Know with certainty the future cash flows.
Ans: (C) Minimize losses.
81. Commercial paper is issued by firms to raise _______. [GSET]
(A) Long-term funds.
(B) Medium-term funds.
(C) Short-term funds.
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (C) Short-term funds.
82. The most common sources of Euro issues include: [GSET]
(A) American Depository Receipts.
(B) Global Depository Receipts.
(C) Both (A) and (B).
(D) None of the above.
Ans: (C) Both (A) and (B).
83. Working capital is also known as: [GSET]
(1) Revolving Capital.
(2) Circulating Capital.
(3) Equity Capital.
(4) Debt Capital.
Select the correct answer from the following:
(A) (3) and (4).
(B) (1) and (2).
(C) Only (3).
(D) (1) and (3).
Ans: (B) (1) and (2).
84. Direct investment in a joint venture abroad can be made by an Indian party without ceiling on limit under automatic route if the investment is made from: [GSET]
(A) balances in EEFC account.
(B) funds raised through ADR/GDR.
(C) balances in EEFC account or funds raised through ADR/GDR.
(D) There is no such provision.
Ans: (C) balances in EEFC account or funds raised through ADR/GDR.
Visit Official Website of Dynamic Tutorials & Services for More MCQs.***


Post a Comment
Kindly give your valuable feedback to improve this website.