[BA 3rd Sem Question Papers, Dibrugarh University, 2015, Mathematics, General, Group - A: Coordinate Geometry and Group - B: Analysis - I (Real Analysis)]
GROUP – A
(Coordinate Geometry)
SECTION – I
(2 –Dimension)
1. (a) Write the condition under which the conic  is non-singular. 1
is non-singular. 1
(b) Find the new coordinates of the point , if the frame of reference is rotated through an angle
, if the frame of reference is rotated through an angle , without changing the origin. 2
, without changing the origin. 2
(c) Find the angle through which it is to be rotated to remove 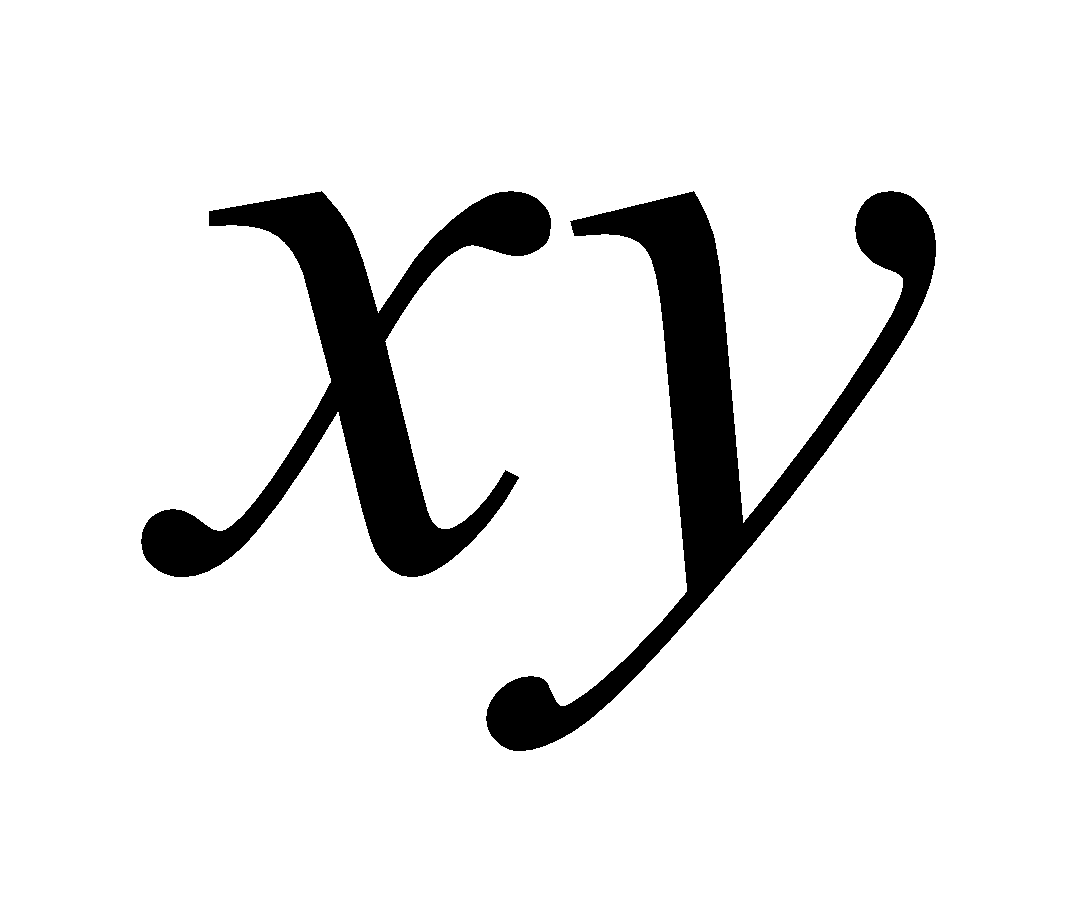 term from
term from . 2
. 2
2. (a)  represents a pair of straight lines. Determine whether they are parallel or perpendicular to each other. 1
represents a pair of straight lines. Determine whether they are parallel or perpendicular to each other. 1
(b) Find the angle between the pair of lines . 2
. 2
(c) Find the pair of lines represented by . 3
. 3
(d) Show that the lines  and
and form an equilateral triangle. 6
form an equilateral triangle. 6
Or
Discuss the nature of the conic represented by the equation
and reduce it to canonical form.
3. (a) Find the equation of tangent at 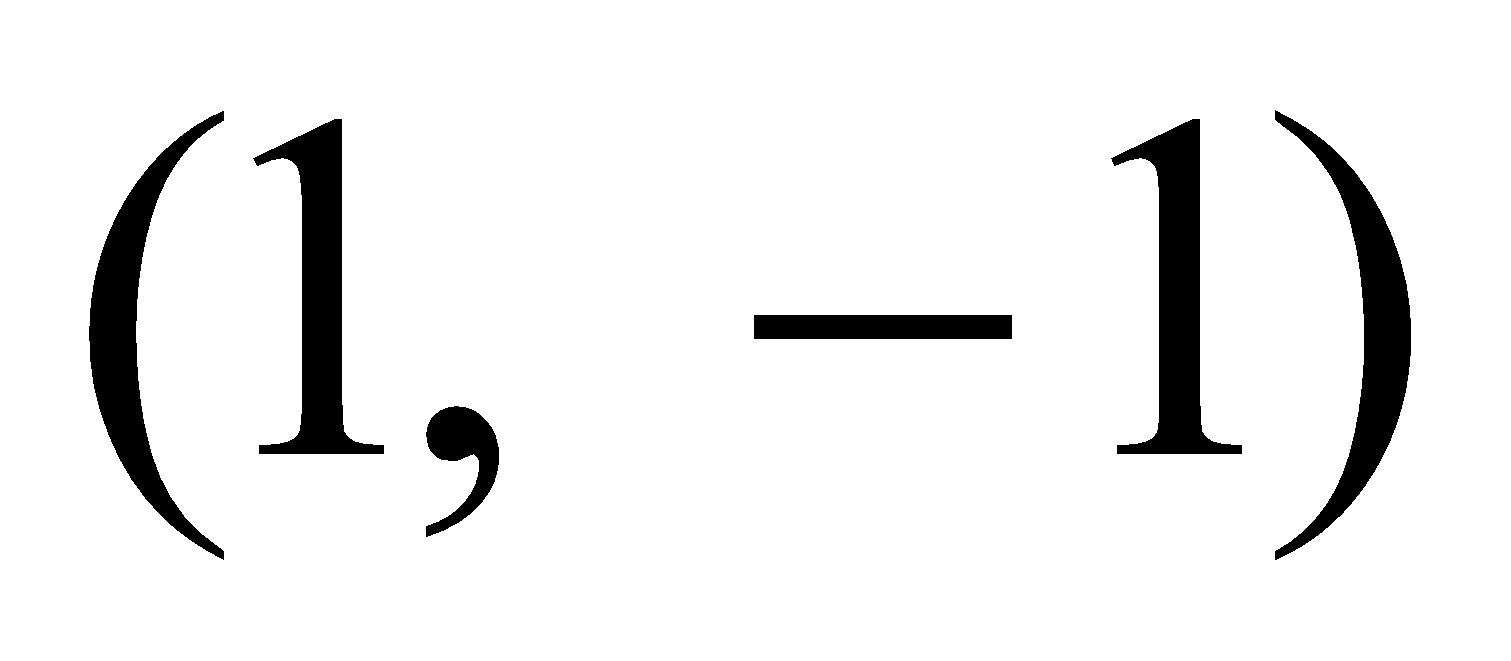 to the conic
to the conic  . 2
. 2
(b) Find the centre of the conic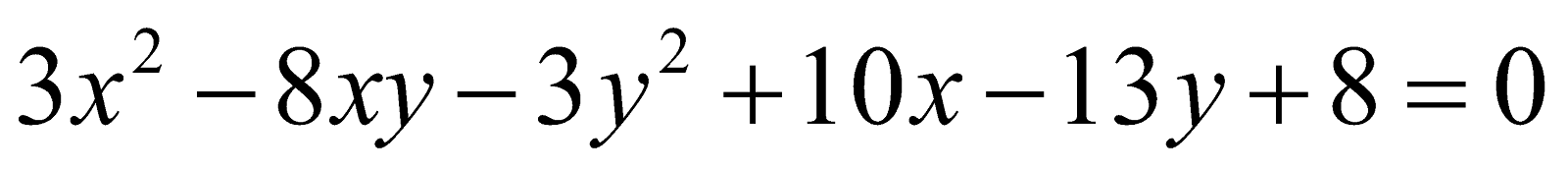 . 3
. 3
(c) Find the pole of a given line with respect to a conic. 5
Or
Determine whether the conic represented by
has a single centre, infinitely many centres or no centre.
SECTION – II
(3-Dimension)
4. (a) Plane is described by an equation. Write the degree of the equation. 1
(b) The plane 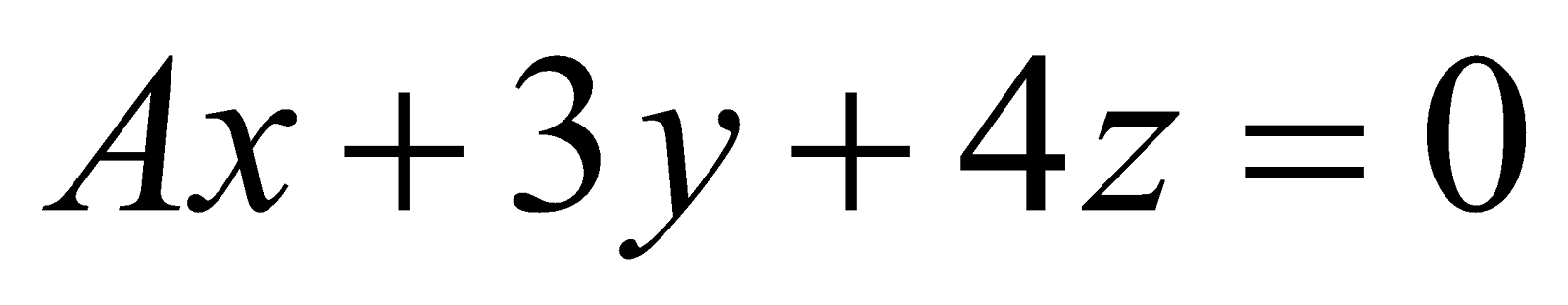 passes through a particular point. Write the coordinates of that point. 1
passes through a particular point. Write the coordinates of that point. 1
(c) Find the intercepts on the axes made by the plane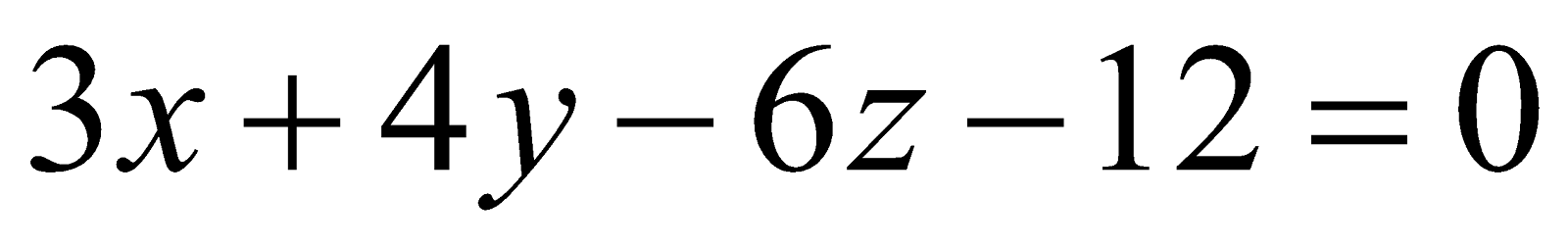 . 2
. 2
(d) Find the equation of the plane passing through the points (3, 1, 1) and (1, -2, 3), and parallel to x-axis. 3
Or
Find the angle between the planes  and
and .
.
(e) Find the equation of the line in symmetric form passing through (2, 0, 4) and (1, -2, 3). 3
5. (a) Find the length of the shortest distance between the following lines: 4
(b) Find the equation of the perpendicular line to the lines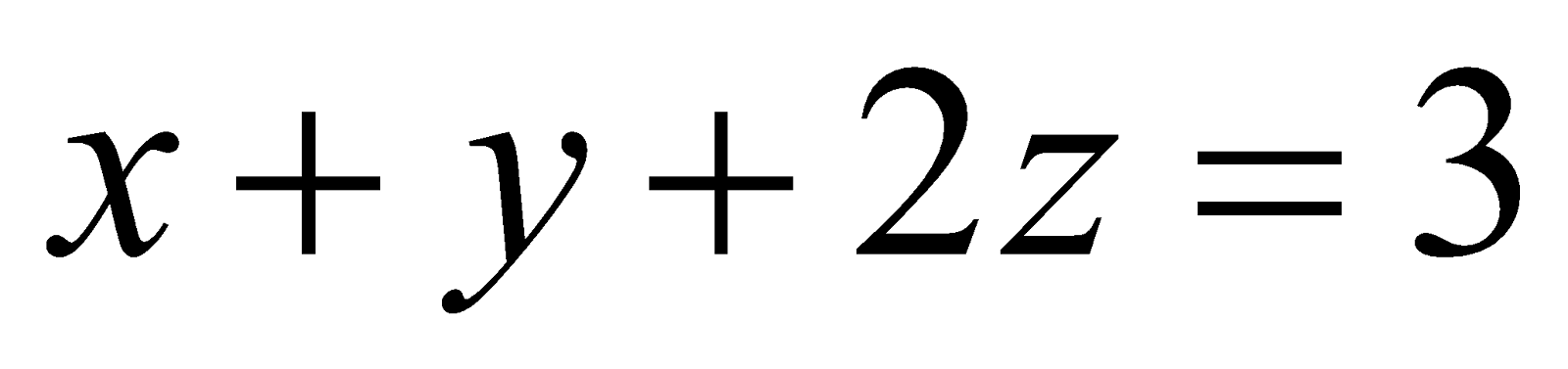 ;
; and z-axis. 4
and z-axis. 4
GROUP – B
(Analysis – I)
6. (a) If 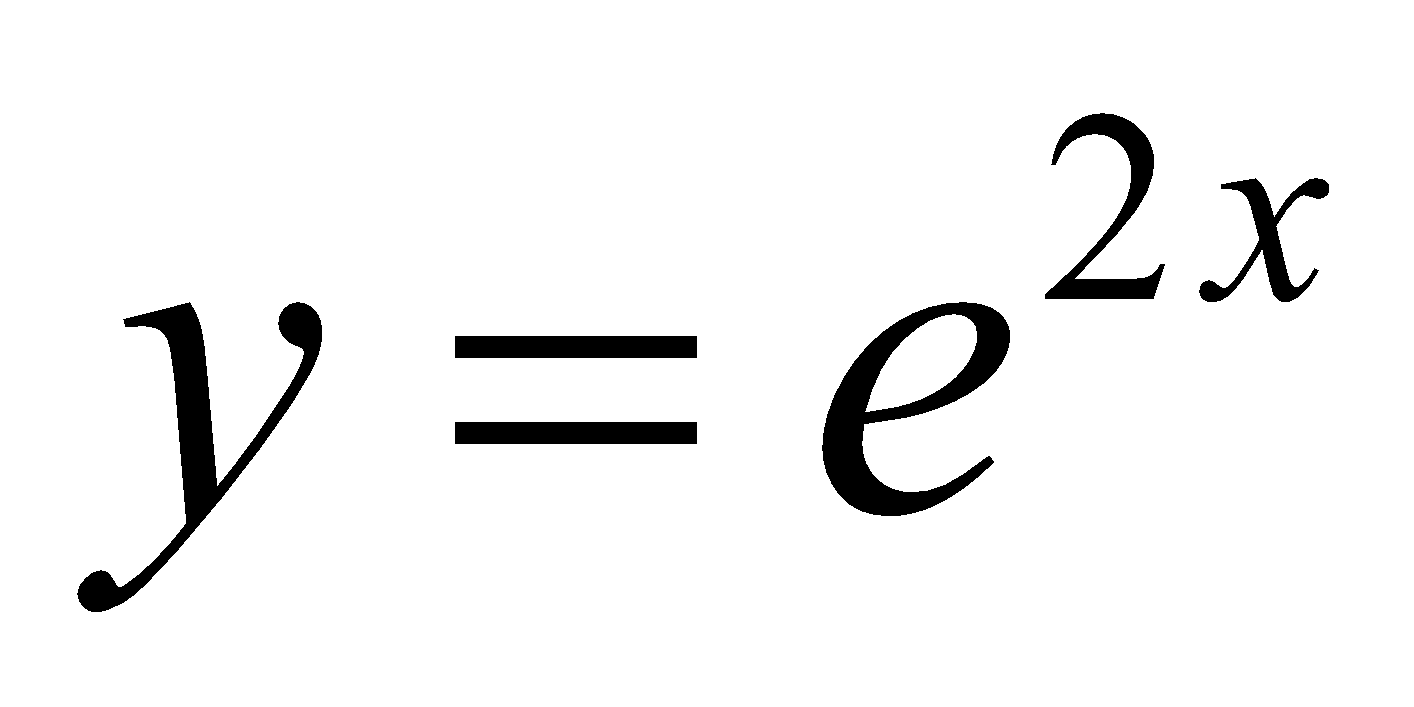 , then find the value of
, then find the value of . 1
. 1
(b) If , then find the value of
, then find the value of . 2
. 2
(c) Find the length of subtangent to 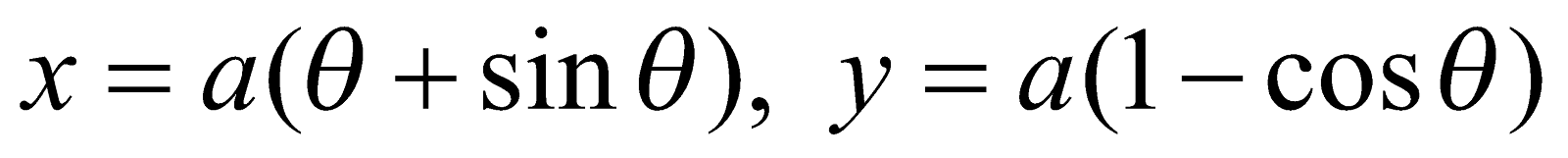 at
at . 3
. 3
Or
Find the radius of curvature of  at any point
at any point .
.
(d) Evaluate any one of the following: 4
7. (a) Write Maclaurin’s theorem with Lagrange’s form of remainder. 1
(b) Write the geometrical meaning of Lagrange’s mean value theorem. 2
(c) Show that a function, which is derivable at a point, is continous at that point. 2
(d) State and prove Rolle’s Theorem. 5
Or
If a function  is derivable on a closed interval
is derivable on a closed interval  and
and ,
,  are of opposite signs, then there exists at least one point
are of opposite signs, then there exists at least one point  between
between  and
and  such that
such that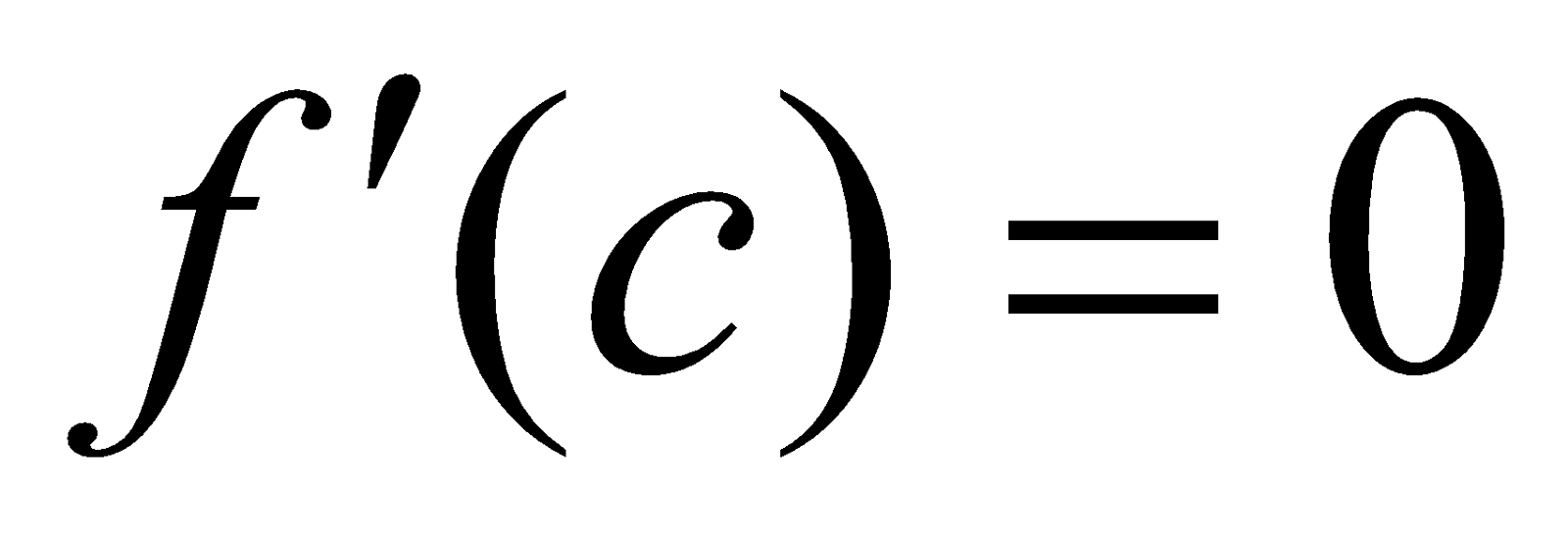 .
.
8. (a) If 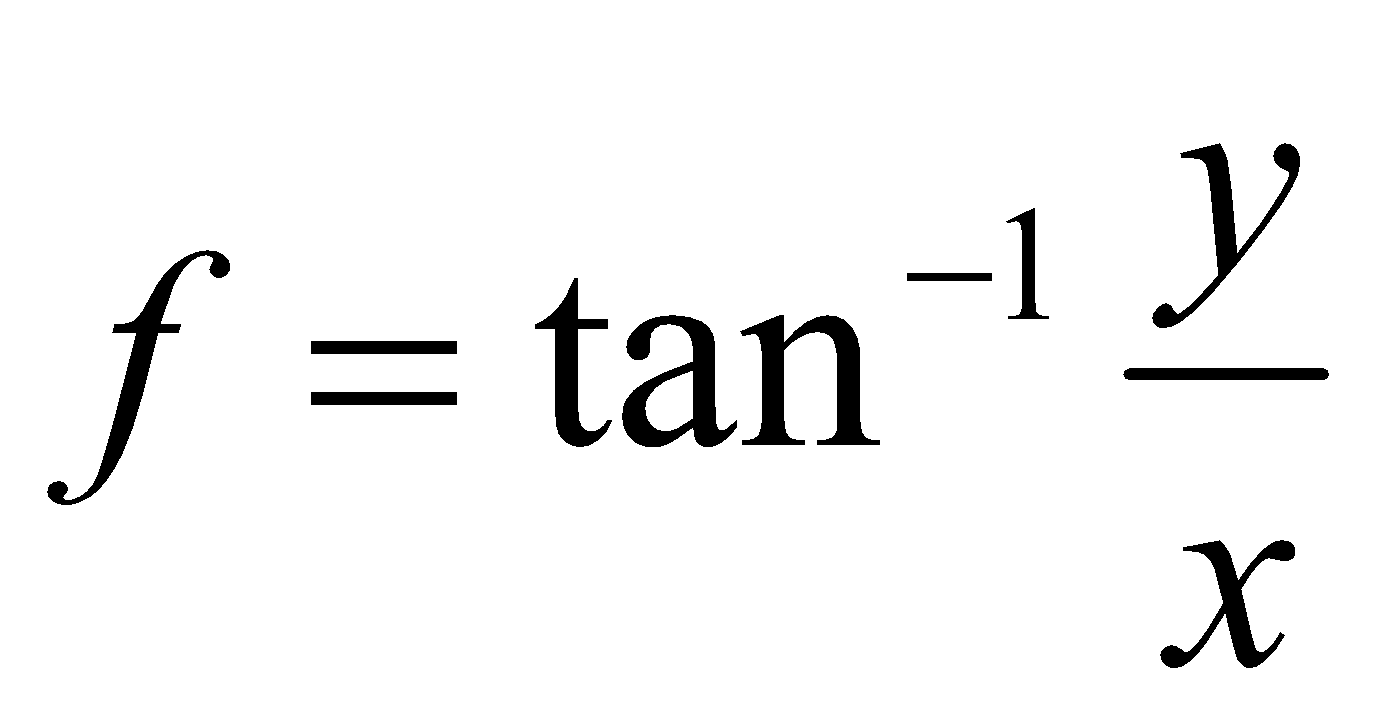 , then find
, then find 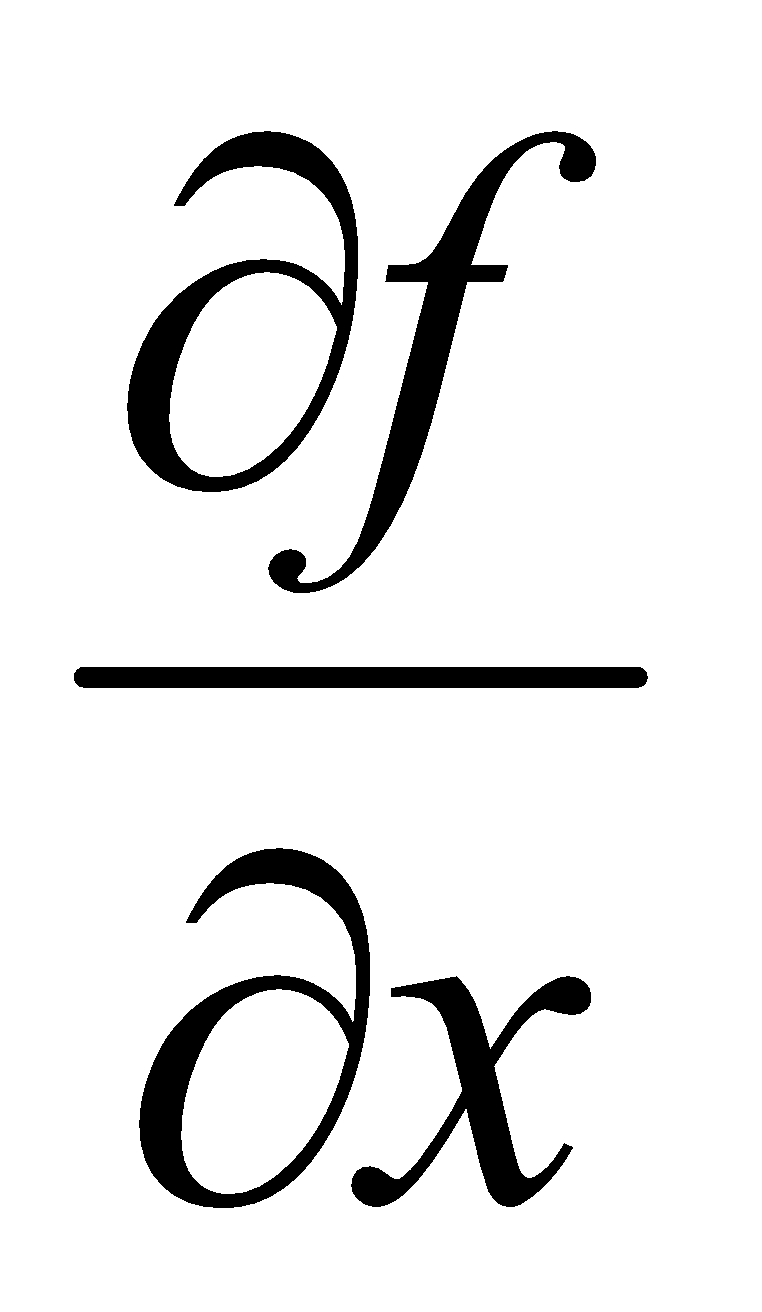 . 1
. 1
(b) Verify Euler’s theorem for . 4
. 4
Or
If 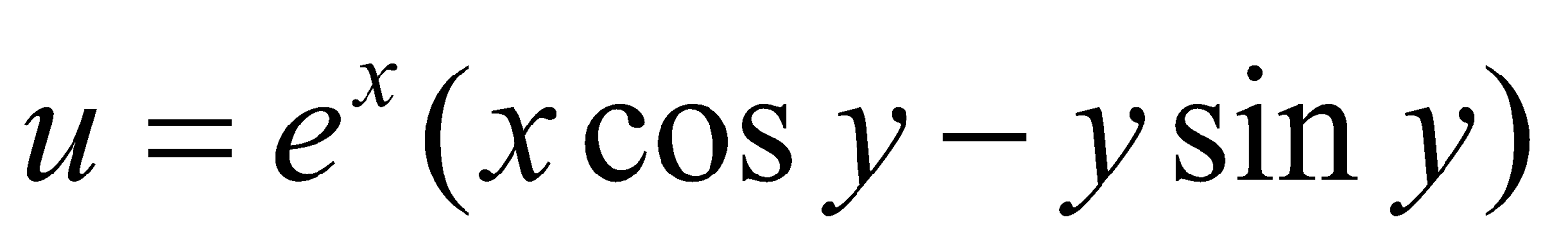 , then show that
, then show that 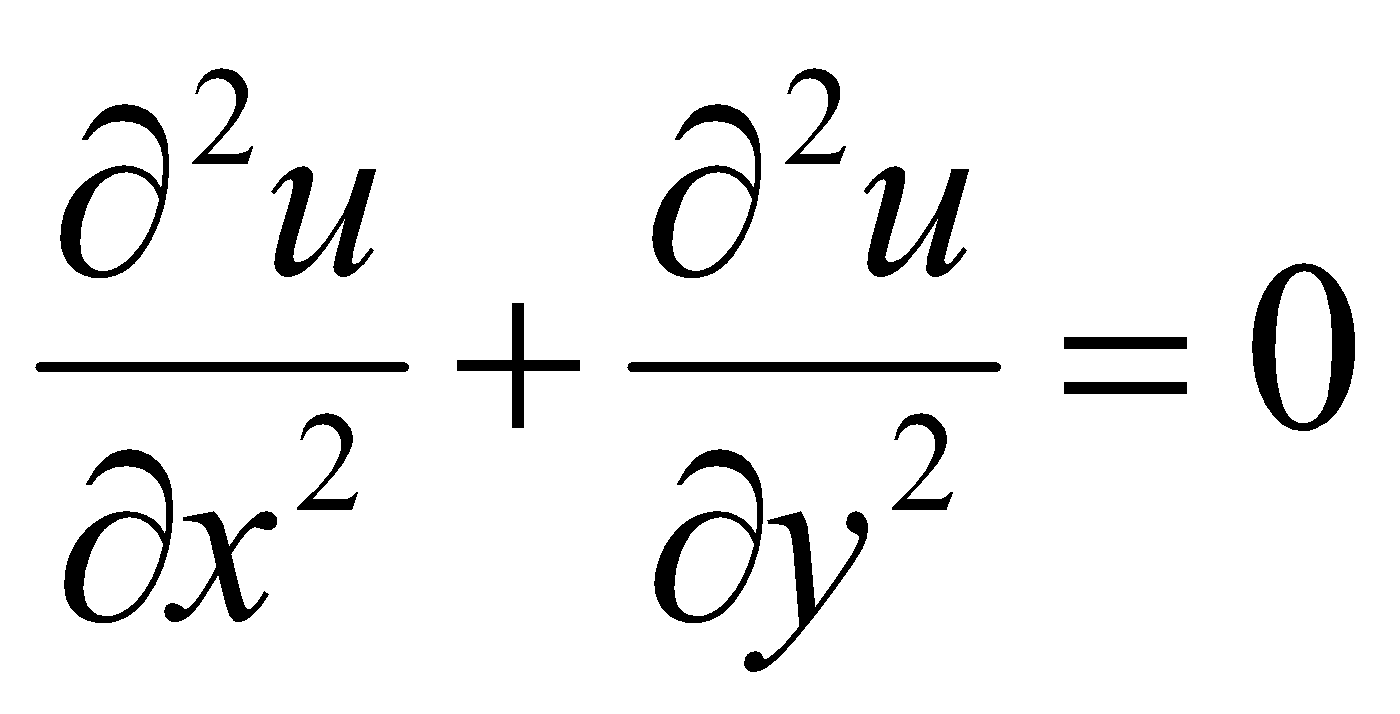 . 1
. 1
Also Read: Dibrugarh University Question Papers
9. (a) Write the condition when  .
.
(b) Evaluate any one of the following: 4
(c) Obtain the reduction formula for . 5
. 5
Or
Find the perimeter of the asteroid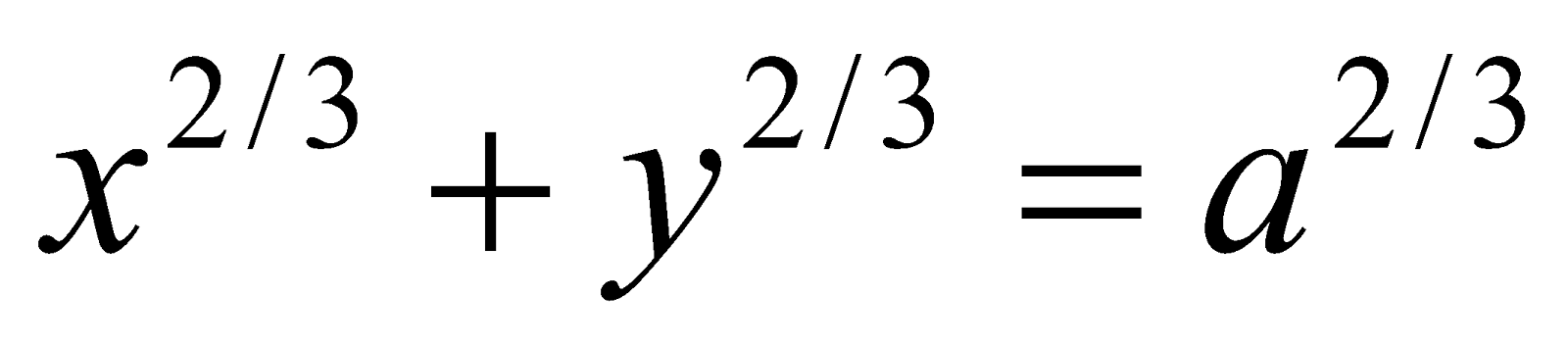 .
.
***


Post a Comment
Kindly give your valuable feedback to improve this website.