GROUP – A
1. (a) Define convex set. 1
(b) Write the mathematical form of a general linear programming problem. 2
(c) Answer any one question:
- Prove that the intersection of two convex sets is again a convex set.
- A firm produces three types of clothes say A, B and C. Three kinds of wools are required for it, say red wool, green wool and blue wool. One unit length of type A cloth needs 2 meters of red wool and 3 meters of blue wool; one unit length of type B cloth needs 3 meters of red wool, 2 meters of green wool and 2 meters of blue wool; and one unit length of type C cloth needs 5 meters of green wool and 4 meters of blue wool. The firm has only a stock of 8 meters of red wool, 10 meters of green wool and 15 meters of blue wool. It is assumed that the income obtained from the one unit length of type A cloth is Rs. 3, of type B cloth is Rs. 5, and that of type of C cloth is Rs. 4. Formulate the problem as linear programming problem.
(d) Answer any one question:
- Solve graphically the following LPP:
Maximize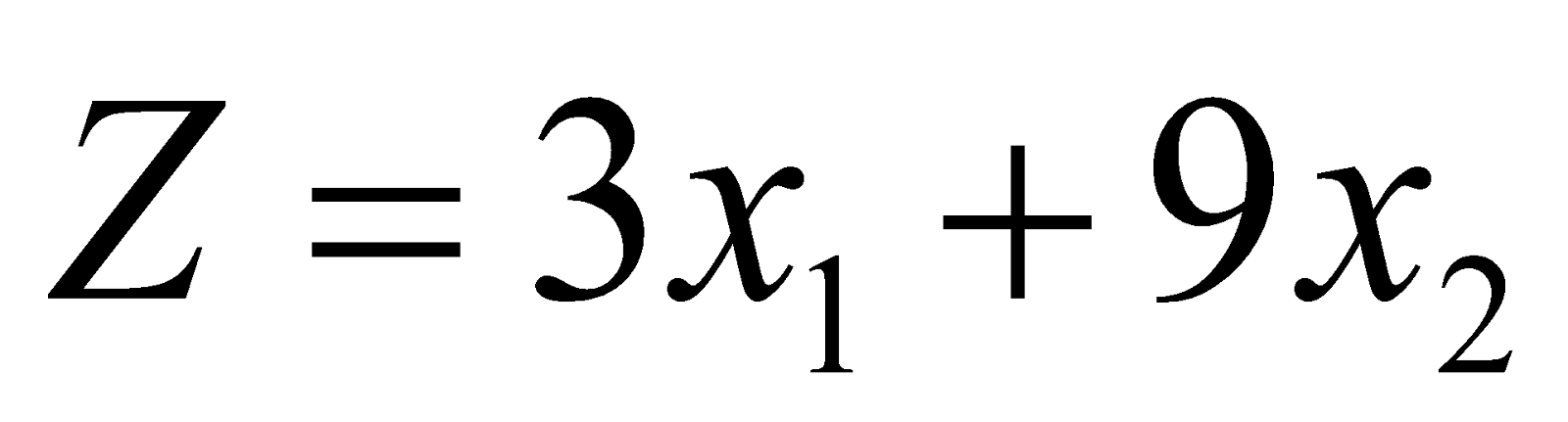
Subject to
And 
- Solve graphically the following LPP:
Minimize
Subject to
And 
2. (a) What do you mean by ‘feasible solution’ of linear programming problem?
(b) Define slack and surplus variables of a linear programming problem.
(c) Answer any one question:
- Using the simplex method, solve the linear programming problem:
Minimize
Subject to
And 
- Discuss the computational procedure of simplex method to solve a linear programming problem.
(d) Answer any one question: 8
- Solve the LPP using two-phase method:
Minimize
Subject to
And 
- Using Big-M method, solve the following LPP:
Minimize
Subject to
And 
3. (a) Write true or false: The dual of a maximization problem is a minimization problem. 1
(b) What do you mean by symmetric primal dual and unsymmetric primal dual and unsymmetric primal dual problems? 2
(c) Answer any one question: 5
- Set up the dual of the following primal problem:
Minimize
Subject to
And 
- Prove that dual of the dual of a given primal is the primal itself.
4. (a) Answer the following questions: 1x2=2
- Define unbalanced transportation problem.
- Define feasible solution of transportation problem.
(b) Define different types of basic feasible solution. 2
Also Read: Dibrugarh University Question Papers
5. Answer any one question: 8
- Obtain an optimal solution using Vogel’s method:
Supply
| |||||
19
|
30
|
50
|
10
|
7
| |
70
|
30
|
40
|
60
|
9
| |
40
|
8
|
70
|
20
|
18
| |
Demand
|
5
|
8
|
7
|
14
|
34
|
- Write short notes on:
- North-West corner rule.
- Vogel’s approximation method.
***


Post a Comment
Kindly give your valuable feedback to improve this website.